Aadhaar Masking vs Data Masking: What is the Difference and Why It Matters?
Aadhaar Masking and Data Masking are two crucial techniques used to protect sensitive information in today’s digital landscape. Aadhaar Masking focuses on securing the widely used 12-digit Aadhaar number by hiding part of it, while Data Masking covers a broader range of personal and financial information by obscuring or replacing sensitive data.
With rising concerns over identity theft, data breaches, and regulatory compliance violations, organizations across industries are increasingly adopting these masking methods to safeguard personal data and build trust with customers.
This guide covers
- Aadhaar masking and data masking
- Its use cases , importance of aadhaar masking and Data masking
- Key differences of aadhaar masking and data masking
- Why masking matters in data security?
Understanding Aadhaar Masking
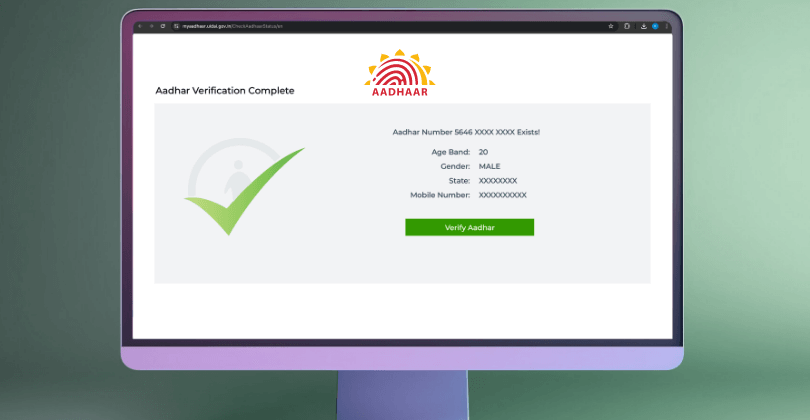
Aadhaar Masking refers to the process of hiding portions of the 12-digit Aadhaar number to prevent unauthorized access and misuse. According to UIDAI guidelines, businesses and government bodies are required to mask the first eight digits of the Aadhaar number, displaying only the last four. This ensures that identity verification can still be conducted while keeping sensitive information secure.
Purpose and Significance
The primary objective of Aadhaar Masking is to reduce the risk of identity theft, fraud, and data misuse. As Aadhaar is used widely in sectors such as banking, telecom, fintech and healthcare, masking helps businesses adhere to privacy laws while facilitating secure KYC (Know Your Customer) processes.
Applications
- Banking:Aadhaar Masking is used during account opening or loan processing, ensuring that customer details remain confidential.
- Telecom:Mobile operators mask Aadhaar data when verifying customer identity for SIM card issuance.
- Insurance:Health insurance providers use masked Aadhaar cards for policy enrollment without exposing complete data.
- Government Services:Masked Aadhaar is used in schemes and subsidies to protect beneficiaries’ privacy.
Aadhaar Masking is thus a targeted approach aimed at safeguarding identity-related data in compliance with regulatory frameworks.
Understanding Data Masking
Data Masking is a broader data protection technique that replaces or obscures sensitive information across databases, applications, and files. Unlike Aadhaar Masking, which focuses on a specific identification number, Data Masking covers a variety of data types such as credit card numbers, medical records, financial statements, and personal addresses.
General Applications
Data Masking is applied in environments where sensitive data must be accessed, tested, or processed without revealing actual information. It is particularly prevalent in:
- Software development and testing: Masking test data to simulate real-world scenarios without exposing live data
- Data analytics: Using masked datasets to conduct analysis while protecting privacy.
- Cloud storage:Masking data before sharing with third party providers to ensure confidentiality.
- Compliance and auditing:Ensuring that organizations meet regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, or Data Protection Bill India.
Role in Privacy and Security
Data Masking helps prevent internal and external data breaches, reduce risk during data transfers, and maintain trust between organizations and their stakeholders. It is a vital tool across industries handling vast amounts of sensitive information
Key Differences Between Aadhaar Masking and Data Masking
Focus of Protection
Aadhaar Masking is specifically designed to protect the 12-digit Aadhaar number by hiding its first eight digits, ensuring that identity verification processes remain secure. In contrast, Data Masking applies to a wide range of sensitive information such as credit card numbers, medical records, financial data, and personal addresses.
Regulatory Requirements
Aadhaar Masking is mandated by UIDAI guidelines and RBI regulations requiring organizations to comply with strict data privacy rules. Data Masking, however, is implemented based on broader industry regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and Data Protection Bill India, depending on the type of data being handled.
Every company in India that accepts and stores Aadhaar cards and photographs, according to the authorized regulatory agencies, must adopt Aadhaar masking. The purpose is to hide the first eight digits of your Aadhaar number from your Aadhaar card and images of your Aadhaar card to protect you from fraud, profiling, and Aadhaar exploitation without your permission.
Use Cases
Aadhaar Masking is primarily used in scenarios involving identity verification, customer onboarding, and government services where Aadhaar serves as proof of identity. Data Masking finds its place in testing environments, analytics, cloud storage, and data sharing processes where privacy and security need to be maintained across various datasets.
Technologies Involved
Aadhaar Masking often relies on AI-powered OCR technology to accurately detect Aadhaar numbers within documents and apply masking rules in real time. Data Masking uses a variety of techniques including encryption, tokenization, substitution, and randomization to mask diverse datasets depending on the organization's security needs.
Data Scope
Aadhaar Masking focuses on protecting a single, highly sensitive identifier, ensuring that personal identity is not compromised. On the other hand, Data Masking covers multiple data elements and fields across different systems, providing comprehensive protection for entire datasets.
Objective and Purpose
The primary goal of Aadhaar Masking is to secure identity information and prevent identity theft, particularly during customer interactions and official transactions. Data Masking, meanwhile, aims to safeguard a broader spectrum of data, helping businesses reduce risks, maintain privacy, and ensure compliance across various operations.While both aim to enhance data security, Aadhaar Masking addresses a niche but highly sensitive dataset, whereas Data Masking is a comprehensive strategy applicable to broader datasets.
Why Masking Matters in Data Security?
Masking is not just about hiding information it is about trust, compliance, and resilience. With sensitive data increasingly targeted by cyber threats, companies need effective masking solutions to protect against misuse.
Protecting Sensitive Information
Masking techniques like Aadhaar and Data Masking prevent attackers from accessing unprotected data, reducing the risk of fraud, phishing, and identity theft. They also limit exposure in cases of internal mishandling or unauthorized access.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Failing to mask sensitive information can lead to severe penalties under UIDAI regulations, RBI circulars, and global data protection laws such as GDPR and HIPAA. Masking not only ensures regulatory compliance but also demonstrates ethical responsibility towards data privacy.
Masking also helps businesses build trust. Customers are more likely to share their personal information if they are confident it’s being handled with care.
Conclusion
Both Aadhaar Masking and Data Masking play vital roles in today’s data-driven ecosystem, but they serve different purposes. Aadhaar Masking protects one of the most important identity credentials in India, ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks while safeguarding individuals’ personal information. Data Masking, on the other hand, provides a versatile method to obscure various types of sensitive data across industries.
Understanding the differences between these techniques is essential for organizations that aim to implement effective data security strategies.
By choosing the right masking solution tailored to specific data types and regulatory requirements, businesses can enhance privacy, prevent misuse, and build digital trust.
In an era where data breaches are frequent and customer expectations are high, distinguishing between Aadhaar Masking and Data Masking and applying them appropriately can make all the difference in protecting sensitive information and ensuring long-term security.